Distributed RPKI monitoring
The Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) is a mechanism to reduce the propagation of routing incidents such as leaks/hijacks (sometimes malicious, many times fat fingers). In the last few years its adoption grew considerably.
If you are starting to adopt RPKI, or if you already adopted it in your network, you will need RPKI monitoring. RPKI monitoring is a fundamental activity to mitigate or to timely correct RPKI misconfiguration that would impact the reachability of your services. For example, in this article NTT highlights how RPKI monitoring was greatly beneficial.
What we alert for
- RPKI-invalid prefix announcements
- Any change affecting your route origin authorizations (ROAs)
- ROAs expiration
- Trust Anchor malfunctions
- RPKI-unknown prefix announcements
By basing our monitoring on BGPalerter, we benefit from years of expertise and reliability in detecting RPKI issues. However, a multi-user solution introduces a new geographically distributed dimension which must be taken into consideration.
In addition to monitoring your operations, PacketVis monitors for RPKI Trust Anchor (TA) failures. A public list of Trust Anchor failures correctly identified by BGPalerter was presented here. Recently, PacketVis alerted its users about two new TA malfunctions, both of them analyzed and confirmed: November 2022, and January 2023 (analysis by Job Snijders). However, a few weeks ago we notified some of our users about yet another malfunction, but this time it was the result of a local failure. The issue was only visible from a node in Singapore. We took this as an opportunity to improve our monitoring and introduce distributed RPKI monitoring.
Nodes used
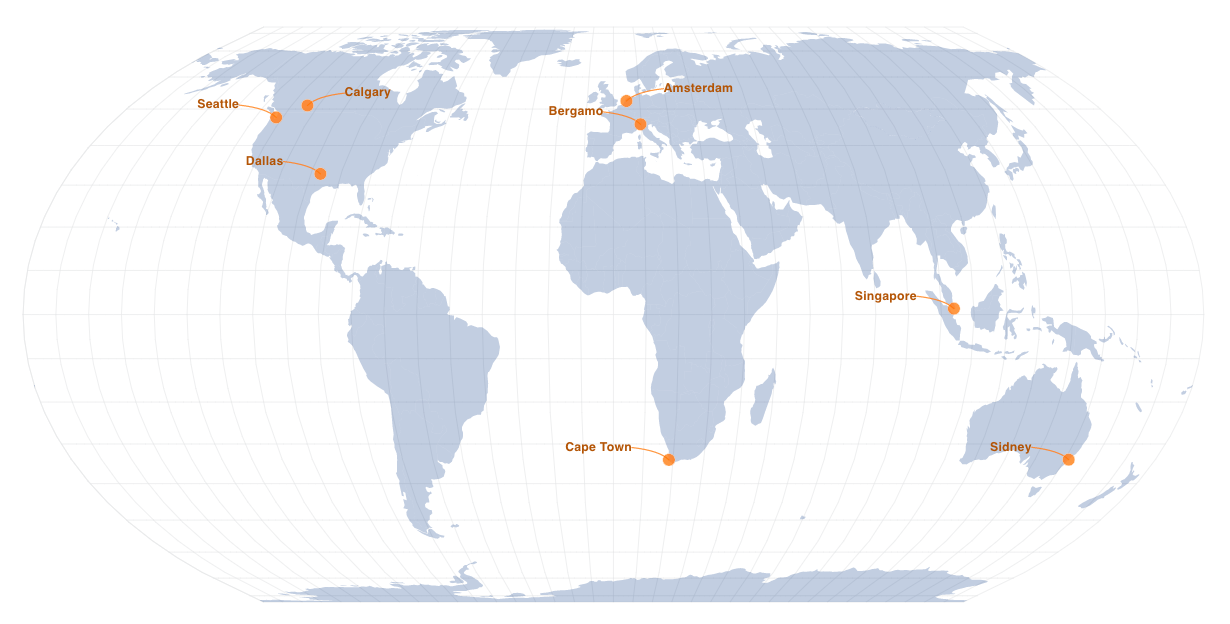
PacketVis will now collect RPKI data from the following nodes (a map is available at the beginning of this post).
| Country | City |
|---|---|
| US | Seattle |
| US | Dallas |
| NL | Amsterdam |
| IT | Bergamo |
| SG | Singapore |
| ZA | Cape Town |
| CA | Calgary |
| AU | Sydney |
The nodes in Seattle and Dallas are hosted by NTT. The nodes in Amsterdam, Singapore, and Calgary are hosted by rpki-client.org.
What changes?
TA malfunctions and disappearing ROAs will now have to be confirmed on at least two nodes on different networks and countries. However, we will internally still be reporting local incidents affecting single nodes, so that they can be manually analyzed.
Moreover, the various hosts perform validation spread in time, with a period that goes from 5 to 15 minutes. This allows us to receive a fresh dataset every ~1 minute, reducing our reaction time to RPKI changes.
Start monitoring your BGP and RPKI operations now!
Enjoy!